Ergonomics and human factors encompass an interdisciplinary field that integrates people, technology, and processes to optimize performance in various organizational settings, such as businesses and corporations. While the terms are often used interchangeably, ‘ergonomics’ is gaining prominence in Indian businesses and will be the preferred term in this discussion. Ergonomics is marked by several key characteristics:
- Systems Approach: It takes a comprehensive view that includes the cultural and physical environment, organizational structure, and specific task demands.
- Design-Driven: Ergonomics focuses on analysis leading to innovative design or redesign of approaches, tools, workplaces, and processes.
- Human-Centered Iteration: Users play a central role, contributing knowledge and testing solutions in an ongoing, iterative process.
- Performance and Well-being Emphasis: It strives to enhance efficiency, effectiveness, health, safety, and job satisfaction, recognizing these as interconnected facets.
Ergonomics is distinct from other fields that concentrate on people, like psychology, sociology, or medicine, in these ways:
- It concentrates on proactive design, including workplace and practice design, to prevent issues from arising, rather than just addressing existing problems.
- It considers the entire system to achieve optimal performance, acknowledging that technology integration alone isn’t effective without accounting for the human factor within the broader context.
- It views overall system performance and well-being as interconnected outcomes, striving to maximize both.
Despite the seemingly common-sense nature of human factors design, numerous human errors, accidents, recalls, and product failures persist. This is often due to neglecting the input of ergonomic specialists. Historical incidents like the Chernobyl disaster, Boeing 737-Max 8 accidents, Bhopal Gas leak tragedy, and Deepwater Horizon oil spill stand as stark reminders of the dire consequences that can arise from disregarding ergonomic principles. Even experienced professionals can overlook potential dangers and prevention methods without proper training.
Ergonomics bridges various disciplines like engineering, medicine, architecture, health and safety, computer science, and consumer product design. It stands as the only scientific field devoted to the interaction between humans and machines. Rooted in extensive knowledge of human attributes and capabilities, it combines engineering expertise to create systems that harmonize with human strengths while accommodating limitations.
Ergonomics draws from psychology (to influence behaviour and design complex systems), biomechanics, and human physiology (to ensure proper user fit) to drive impactful changes in technological and workflow design, averting errors and accidents while elevating worker productivity.
Historically, ergonomics evolved to address the swift design of intricate systems. In modern times, ergonomists play a vital role within design teams, offering valuable insights into human behaviour and needs, which may be scarce within many organizations. They ensure all aspects of a system are assessed from the user’s or operator’s perspective, aligning with the core essence of ergonomics.
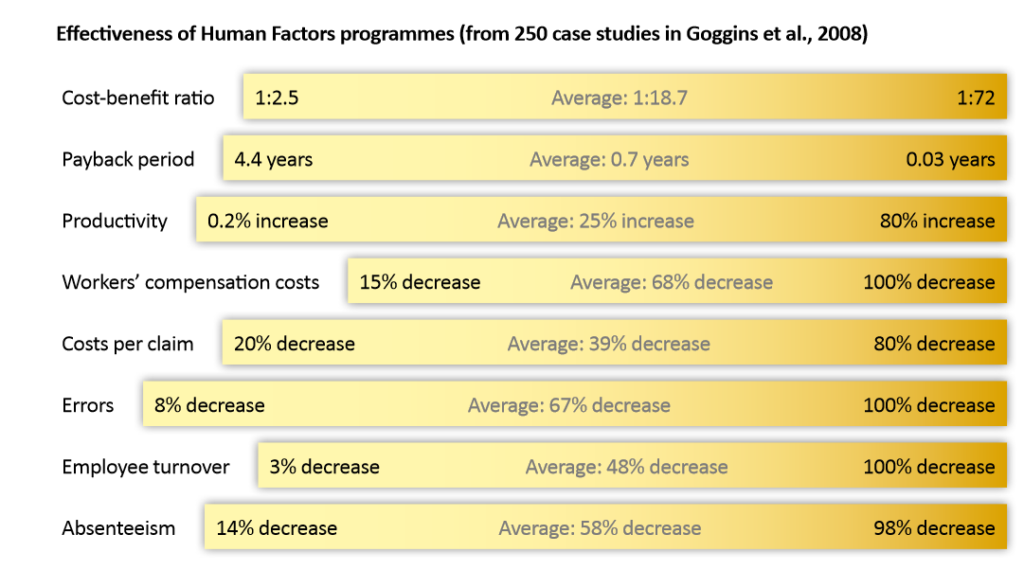
Ergonomics uses successfully tested techniques that can be adopted across almost any industry.



